July 4 , 2024
“Renewable Energy can propel the nation to net zero”
Earth's temperature has risen by approximately 1.1°C since the late 1800s.
Progress towards net zero could potentially avoid 2.7°C of
global temperature increase
Net Zero refers to eliminating or balancing Greenhouse Gas
emissions and other environmentally damaging human activities
through carbon storage and sequestration.
Let us investigate the details of the net zero emissions target
To mitigate severe climate impacts and preserve our planet, we must limit global warming to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels. Currently, Earth's temperature has risen by approximately 1.1°C since the late 1800s. Under the Paris Agreement, the goal is a 45% reduction in emissions by 2030 and achieving net zero by 2050. The Paris Agreement is a legally binding international treaty on climate change. It was adopted by 196 Parties at the UN Climate Change Conference (COP21) in Paris, France, on December 12, 2015.
Despite commitments from over 140 countries and thousands of institutions within the Race to Zero initiative, existing climate plans are insufficient, projecting a near 9% rise in emissions by 2030 from 2010 levels ( UN )
Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs):
Achieving net zero necessitates profound transformations in our energy, industrial, and transportation sectors, urging top emitters to intensify their Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) and enact immediate emission reductions. The Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) are commitments made by countries to reduce their greenhouse gas emissions to mitigate climate change. These commitments outline the necessary policies and measures to achieve the global targets established in the Paris Agreement. NDCs play a crucial role in international climate efforts, as they specify each country's plans and actions to contribute to the collective goal of limiting global warming to well below 2°C, with efforts to limit it to 1.5°C. By implementing these contributions, countries aim to foster sustainable development while addressing the urgent need for climate action.
Progress towards net zero could potentially avoid 2.7°C of global temperature increase and avoid 24 gigatons of additional carbon dioxide emissions by 2050 (International Energy Agency)
India’s cumulative renewable capacity reached 191.65 GW by March 2024, with solar energy leading at 43% of the mix
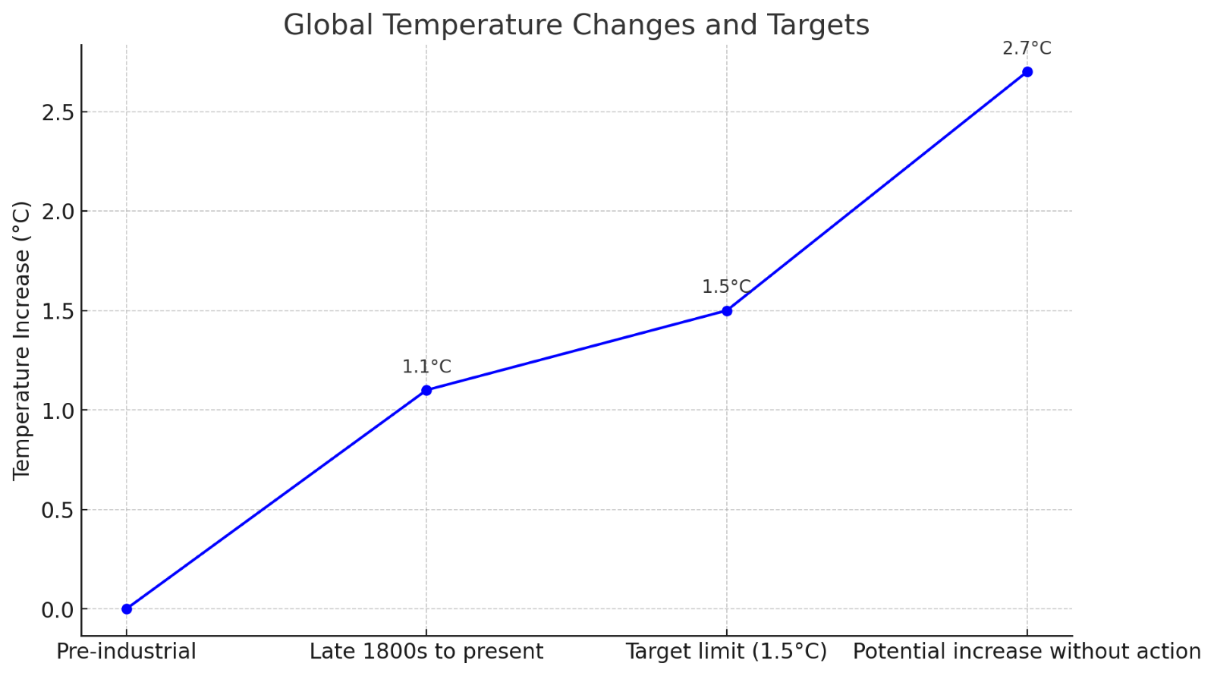
The graph illustrates the urgency of addressing climate change to prevent exceeding critical temperature thresholds.
A growing coalition of countries, cities, businesses, and other institutions is pledging to achieve net-zero emissions. Over 140 countries, including major polluters like China, the United States, India, and the European Union, have set a net-zero target, encompassing about 88% of global emissions. More than 9,000 companies, over 1,000 cities, over 1,000 educational institutions, and over 600 financial institutions have joined the Race to Zero, committing to take rigorous, immediate action to halve global emissions by 2030 ( UN )
At the 26th session of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (COP 26) in November 2021, India announced its ambitious target to achieve net zero emissions by 2070, joining numerous other countries in committing to similar goals for a sustainable future.
Renewable Energy Projects in India, 2024
India is making significant strides towards achieving net-zero carbon emissions by 2070, with a focus on scaling up renewable energy projects.
Here's an overview of some recent initiatives and plans:
To initiate projects in renewable energy, the government has set an ambitious goal of achieving 500 GW of installed renewable energy capacity by 2030 (times of India).
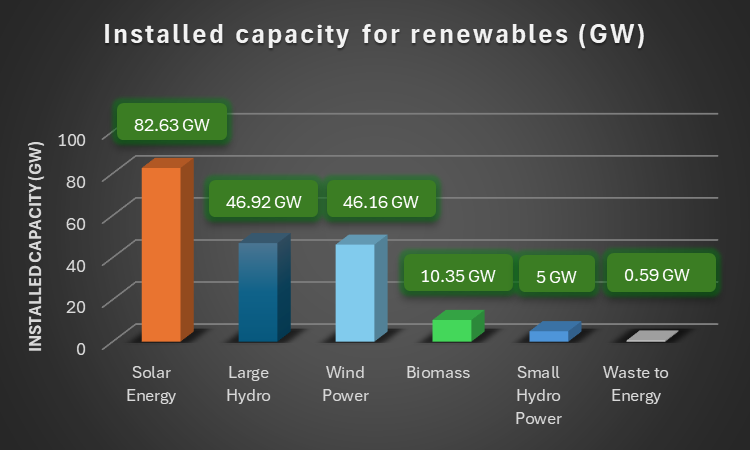
(Numerical data source: MNRE, PIB)
India has recently made substantial progress in the development of renewable energy. The country's cumulative renewable capacity reached 191.65 GW by March 2024, with solar energy leading at 43% of the mix. The National Green Hydrogen Mission, with a ₹19,744 crore investment, aims to produce 5 MMT of green hydrogen annually by 2030. Wind energy capacity is set to reach 140 GW, and new projects like floating solar plants on dams are underway.
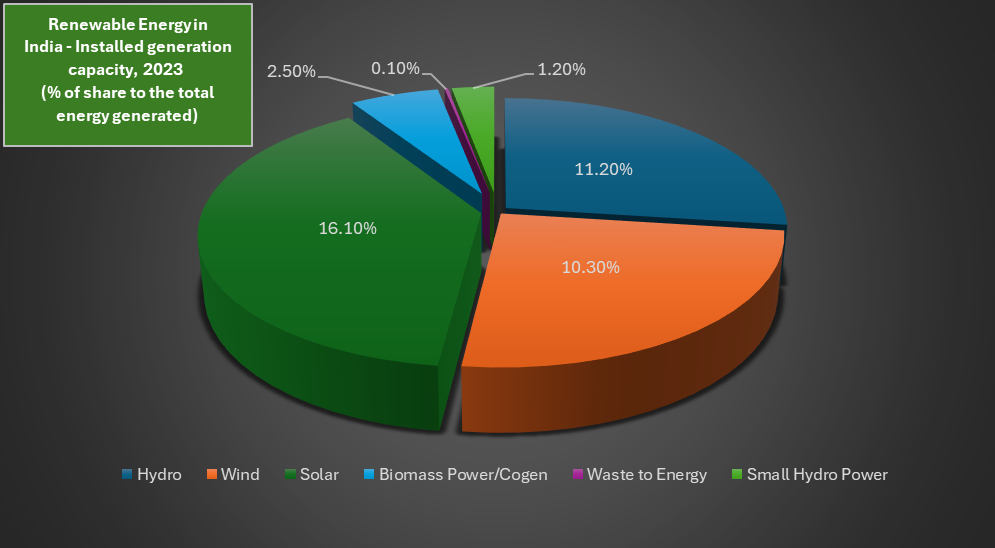
(Numerical Data Source: Ministry of Power )
The government’s initiatives also include promoting electric vehicles, enhancing grid modernization, and encouraging private sector investment, positioning India as a leader in the global renewable energy landscape. The recent developments related to renewable energy are listed below:
| Initiative | Goal | Highlights |
|---|---|---|
| Green Hydrogen Mission | Develop green hydrogen production to decrease reliance on fossil fuels and reduce carbon emissions in heavy transport. | India launched the National Green Hydrogen Mission with an allocation of ₹19,744 crore to develop at least 5 MMT per annum by 2030. |
| National Solar Mission | Expand solar energy capacity to reduce dependency on coal and fossil fuels. | Aiming for 280 GW by 2030, India already achieved over 53 GW, significantly contributing to the renewable mix. |
| Wind Energy Projects | Increase wind energy production to harness India's significant wind energy potential. | India has plans to reach 140 GW by 2030, with current capacity around 43 GW. |
| Hydropower Development | Develop both large and small hydropower projects to provide stable, renewable energy. | India focusses on enhancing the current capacity of about 50 GW. |
| Floating Solar Projects | Utilize water bodies to optimize land use and generate solar power. | Floatovoltaics includes projects like the floating solar plant on Omkareshwar Dam (600 MW) and Rihand Dam. |
| Renewable Energy Parks | Establish large-scale parks to minimize land acquisition issues and boost renewable generation. | Renewable energy parks including Dholera Solar Park in Gujarat and Bhadla Solar Park in Rajasthan, with Bhadla having nearly 2.25 GW capacity are approved by the government. |
| Electric Mobility Initiatives | Transition to EVs to reduce emissions from the transport sector. | The Indian government provides support through incentives like the FAME scheme to boost EV adoption. |
| Bioenergy Projects | Develop bioenergy from agricultural waste to provide renewable alternatives to natural gas. | India has planned to work on projects that focus on producing biogas and bio-CNG. |
| Grid Modernization | Effectively integrate renewable energy into the national grid. | India is constantly upgrading infrastructure to include energy storage systems and smart grids. |
| Policy Support | Create a favorable environment through supportive policies. | India has planned to Implement Renewable Purchase Obligation (RPO), energy certificates, and subsidies. |
| Energy Efficiency Improvements | Increase efficiency and reduce energy consumption. | India has started initiatives like the PAT scheme and UJALA for affordable LEDs. |
(Numerical Data Source: MNRE, PIB )
India's approach targets the expansion of renewable energy capacity while addressing the integration and efficiency of renewable sources within the national grid. The strategic emphasis on reducing dependency on fossil fuels and fostering technological innovation positions India as a leader in the global renewable energy landscape, driving towards the goal of net-zero emissions by 2070. Furthermore, the initiatives outlined provide a replicable model for other nations aiming to achieve similar environmental and economic benefits through renewable energy adoption.

