July 18, 2024
India's Solar Breakthrough: 748 GW from Wasteland to Energy Hub
The National Institute of Solar Energy (NISE) estimates that India has a solar potential of approximately 748 GW, using just 3% of the country's wasteland
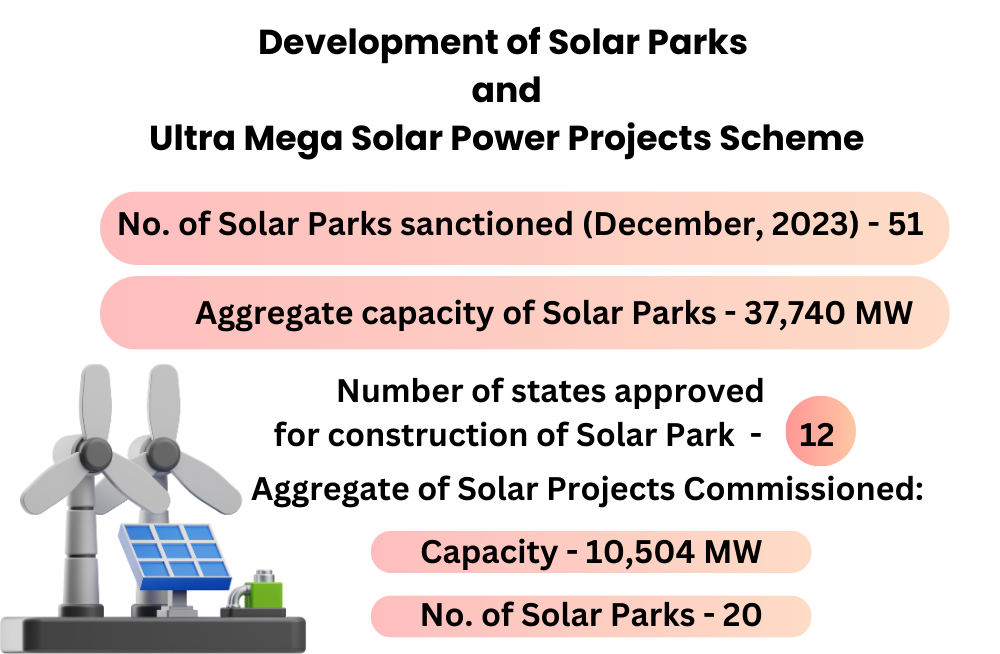
Government has sanctioned 51 Solar Parks with a total capacity of 37,740 MW across 12 states
Driven by innovative policies and initiatives like the National Solar Mission, India is rapidly advancing towards sustainable growth and energy security, significantly contributing to global climate change mitigation efforts.
Let us explore India's dynamic solar energy landscape
The National Institute of Solar Energy (NISE) has estimated that India has a solar potential of approximately 748 GW, based on the assumption that 3% of the country's wasteland area is utilized for Solar PV modules.
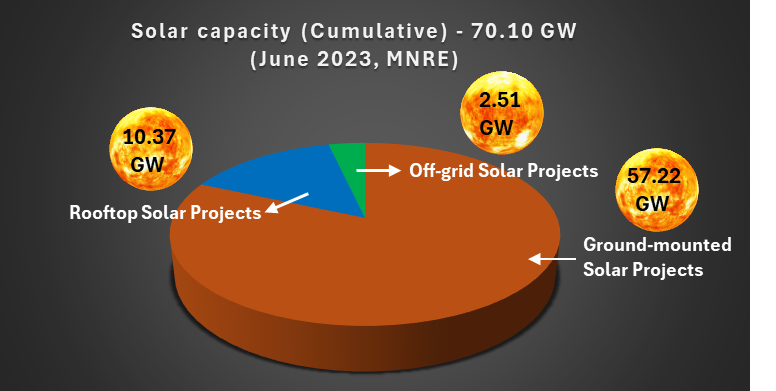
India aims to achieve 280 GW of solar capacity by 2030. The installed solar energy capacity has increased 30-fold over the past nine years, reaching 70.10 GW as of June 2023.
Floating solar plants, also known as floatovoltaics, can be up to 30% more efficient than land-based solar panels
The NSM aims to create favorable policy conditions for the rapid diffusion of solar technology across India. This aligns with India's Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) target:
-
Achieve 50% cumulative electric power installed capacity from non-fossil fuel-based energy resources by 2030
-
Reduce emission intensity of GDP by 45% from 2005 levels by 2030.
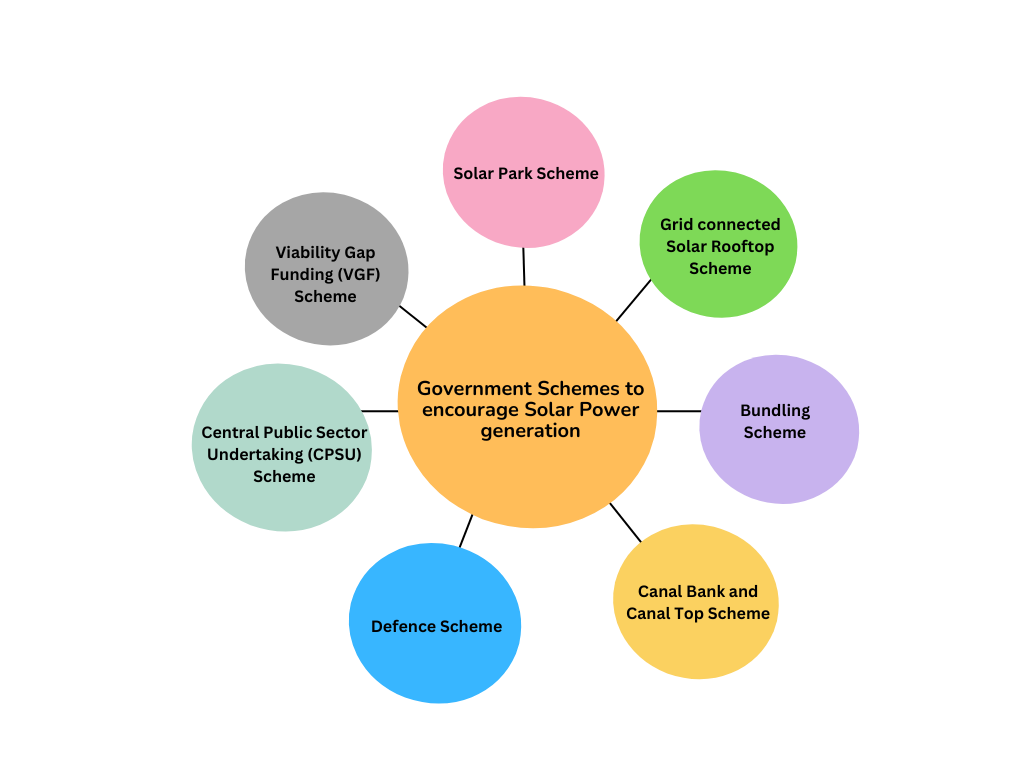
Government schemes and policies:
The government schemes are part of the government's efforts to boost solar power generation and achieve the ambitious targets set under the NSM and NDCs.
The 'Rooftop Solar Scheme,' also known as the 'PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana,' was announced in the 2024-25 budget. This scheme offers subsidies for installing rooftop solar panels on residential houses, enabling homeowners to use solar energy for electricity and reduce their electricity bills.
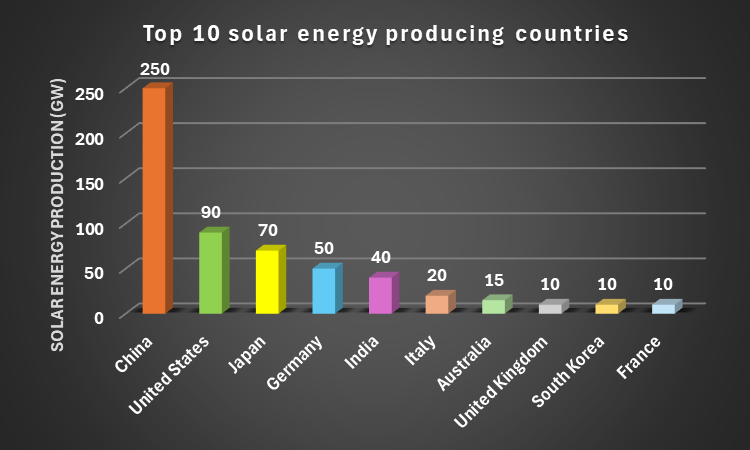
The global move towards renewable energy is boosting solar power production. Governments and international organizations are offering trade tariffs, incentives, and subsidies to attract investors. China is the leading solar energy producer, followed by the United States, Japan, Germany and, India (iea.org)
Role of NISE:
-
The National Institute of Solar Energy (NISE) under the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE), India, focuses on R&D, solar component testing, certification, capacity building, and solar product development.
-
Supporting MNRE's goal of renewable energy and self-reliance, NISE addresses National Solar Mission (NSM) challenges.
-
Through innovation and development, NISE advances the solar energy sector, working closely with the Government of India to accelerate renewable energy growth.
Floating Solar Projects:
The objective of Floating solar or Floating photovoltaics (FPV) or Floatovoltaics is to utilize water bodies to optimize land use and generate solar power
The Government of India aims for 280 GW of solar capacity, requiring six lakh hectares of land. Due to land scarcity, CPSUs and private companies are shifting to floating solar projects. In land-based solar projects, land acquisition is time-consuming and often causes significant project delays. Floating solar or floatovoltaics, though 15-30% costlier, offers 10% higher efficiencies as the water cools the panels.
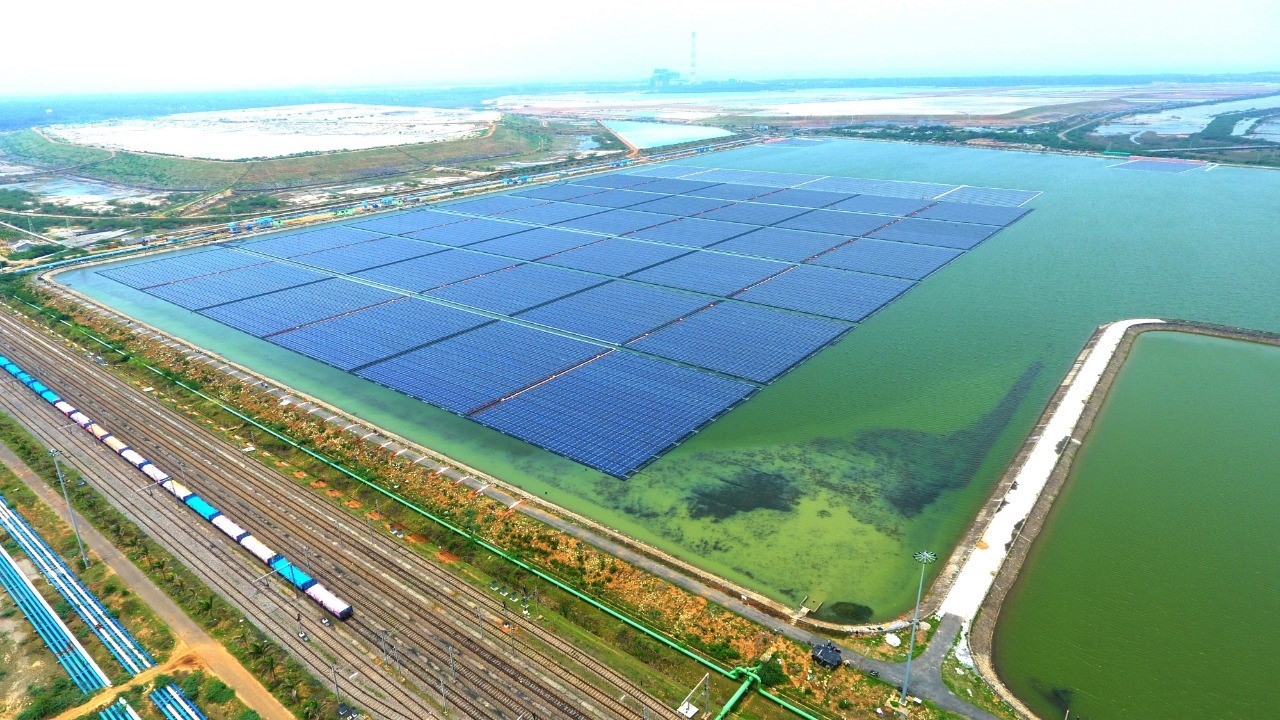

NTPC Floating Solar Plant Ramagundam (100 MW) - The biggest Floating Solar project in India (National Thermal Power Corporation)
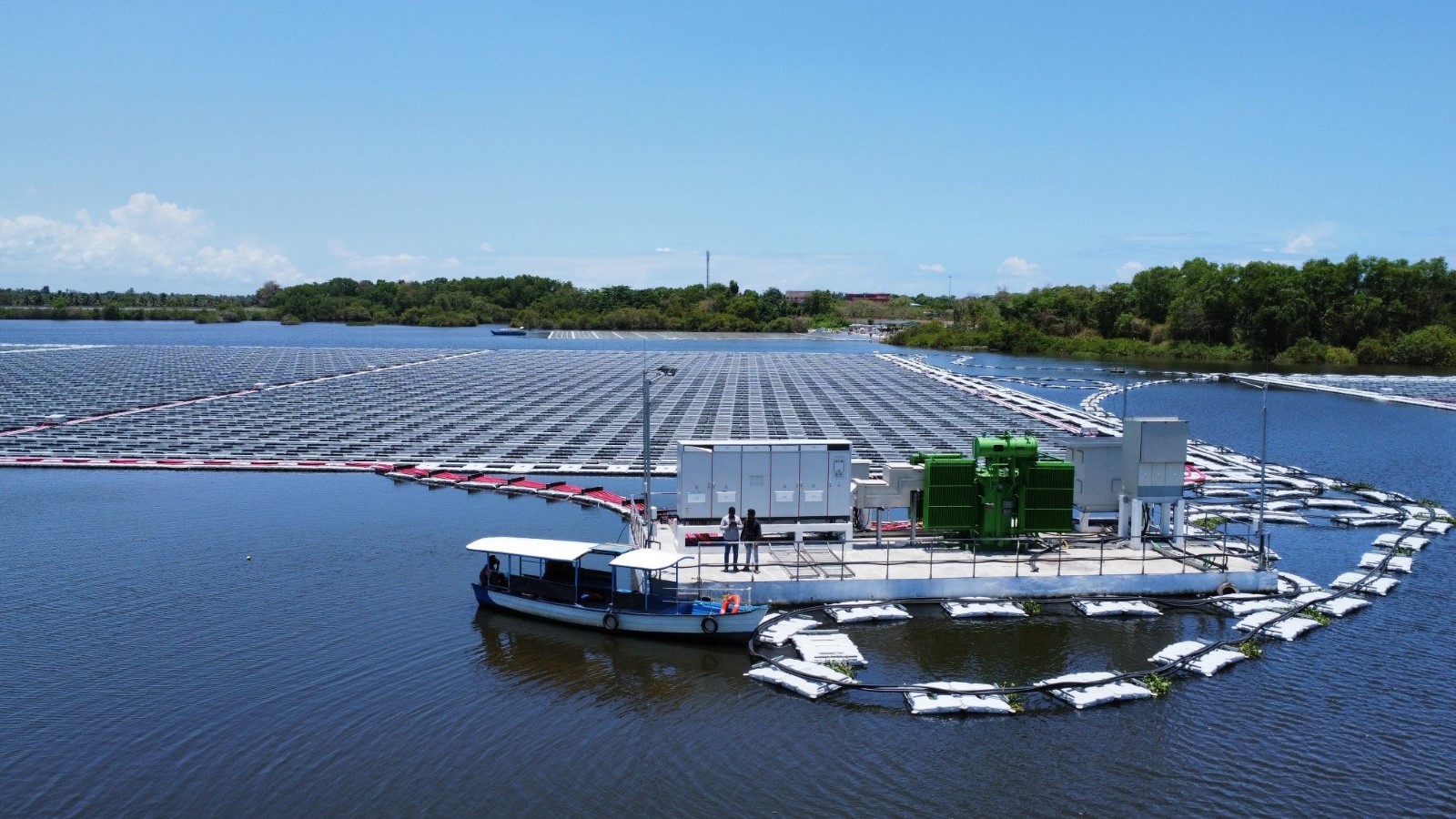

NTPC Floating Solar Plant Kayamkulam (92 MW) - (pv magazine)

Rihand Dam Floating Solar Power Plant (50 MW) - (energetica india)
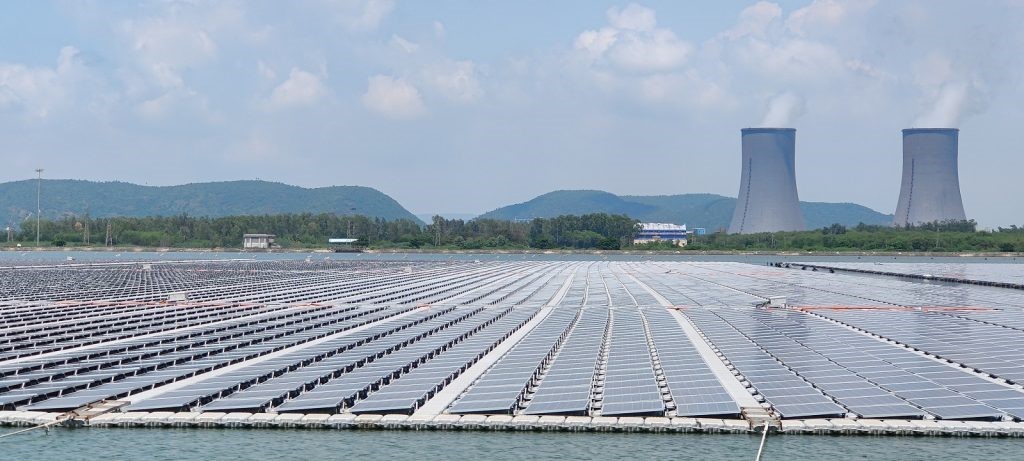

Simhadri Floating Solar PV Project (25MW) - (National Thermal Power Corporation)

2 MW Floating Solar Power Plant at Chandigarh - (Solar Quarter)
Renewable Energy Parks:
Renewable energy parks are large-scale parks established to minimize land acquisition issues and boost renewable generation. The Bhadla Solar Park, one of the largest in the world, has a total capacity of nearly 2.25 GW.
The “Development of Solar Parks and Ultra Mega Solar Power Projects” Scheme (MNRE) facilitates the solar project developers to set up renewable/solar energy projects expeditiously.
According to MNRE, the scheme has an approved allocation of Rs. 8,100 Crores and was extended to FY 2025-26 without any additional financial implications.
It is reported that the Government has sanctioned 51 Solar Parks with a total capacity of 37,740 MW across 12 states. Of these, 11 Solar Parks with a combined capacity of 7,521 MW have been completed, and 7 Solar Parks with a combined capacity of 2,983 MW are partially completed. In total, solar projects with a capacity of 10,504 MW have been developed within these parks. The electricity generation capacity of solar projects in these parks has increased by 2,292 MW over the last three years before August 2023.

(Numerical Data source: Press Information Bureau, Invest India )
India's solar energy sector has rapidly advanced, and this growth is driven by photovoltaic (PV) technologies and innovations. India’s strategic initiatives, such as the National Solar Mission and state-specific policies, foster investment, and development. Advanced energy storage solutions and smart grid integration ensure reliability and stability. Leveraging vast solar resources, India is poised to meet its renewable energy targets, significantly reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and enhancing energy security.

